Iron Fe
Iron is the 26 element in periodic table situated in 4 period.| Symbol | Fe |
| Number | 26 |
| Atomic weight | 55.8450000 |
| Latin name | Ferrum |
| English name | Iron |
Electronic configuration of of Iron
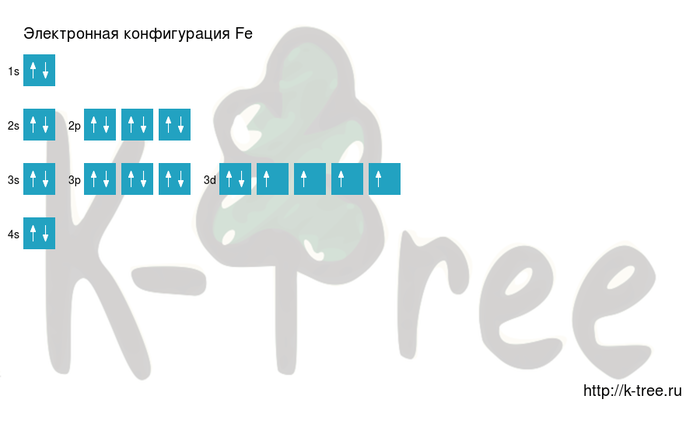
Fe: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6
Short notation:
Fe: [Ar]4s2 3d6
Same electronic configuration has an atom of Iron and Mn-1, Co+1, Ni+2
The order of filling the shells with electrons of Iron (Fe): 1s → 2s → 2p → 3s → 3p → 4s → 3d → 4p → 5s → 4d → 5p → 6s → 4f → 5d → 6p → 7s → 5f → 6d → 7p.
On the sub level ‘s’ there might be 2 electrons at most, on ‘p’ - up to 6, on ‘d’ - up to 10 and up to 14 on ‘f’
Iron has 26 electrons, let's fill electronic layers in described order:
2 electrons on 1s-sub level
2 electrons on 2s-sub level
6 electrons on 2p-sub level
2 electrons on 3s-sub level
6 electrons on 3p-sub level
2 electrons on 4s-sub level
6 electrons on 3d-sub level
Oxidation state of Iron
Atoms of Iron in compounds have an oxidation state of 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, -1, -2.
The oxidation state is the conditional charge of an atom in a compound: the bond in a molecule between atoms is based on the sharing of electrons, thus, if the atom’s charge virtually increases, then the oxidation state is negative (electrons carry a negative charge), if the charge decreases, then the oxidation state is positive.
Ions of Iron
Valence of Fe
Atoms of Iron in compounds have valence VI, V, IV, III, II, I.
Valence of Iron is an ability of an atom Fe to build chemical bounds. The valence is based on electronic configuration of atom: electrons participated in chemical bounds are known as valence electrons. In general the valence is:
The number of possible chemical bounds with other atoms
The valence has no sign.
Quantum numbers Fe
Quantum numbers are defined by the last electron in configuration, for an atom Fe these numbers are N = 3, L = 2, Ml = 3, Ms = -½
Filling an electronic configuration (gif):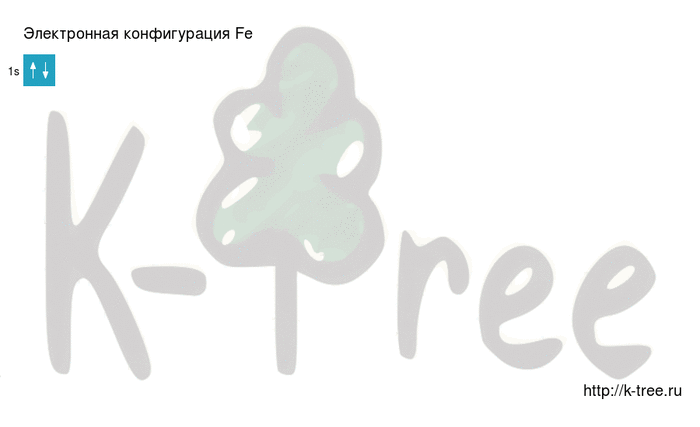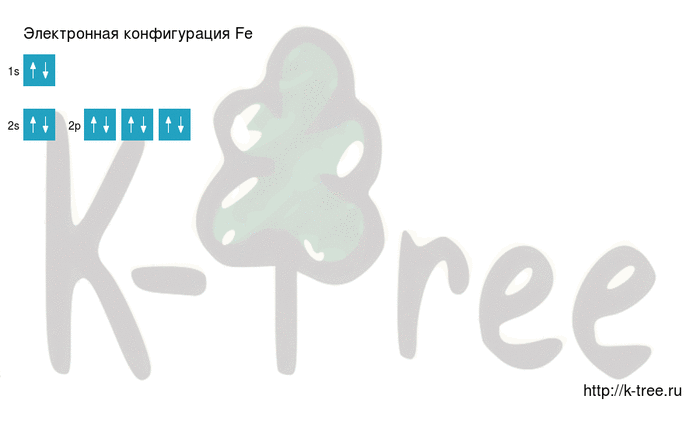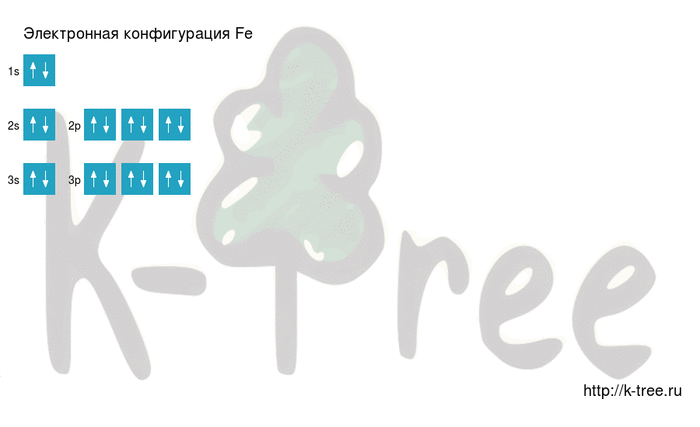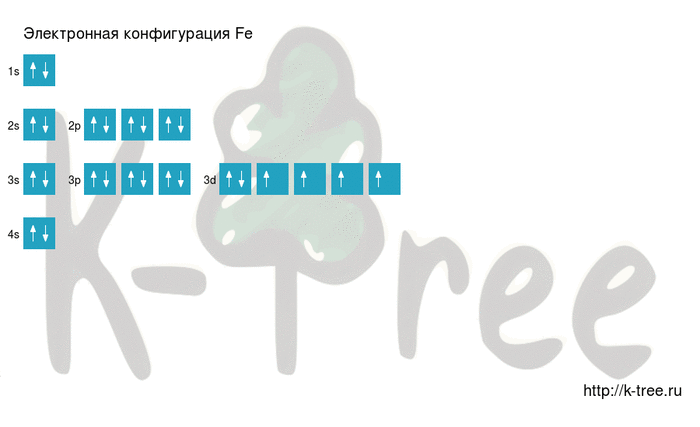
Result:
Ionization energy
The closer the electron is to the center of the atom, the more energy is needed to tear it off. The energy spent on removing an electron from an atom is called ionization energy and is designated Eo. Unless otherwise stated, the ionization energy is the energy of removal of the first electron, and there are also ionization energies for each subsequent electron.
Ionization energy of Fe:
Eo = 763 kJ/mol
See all elements of the periodic table
Where is Fe in the periodic table?